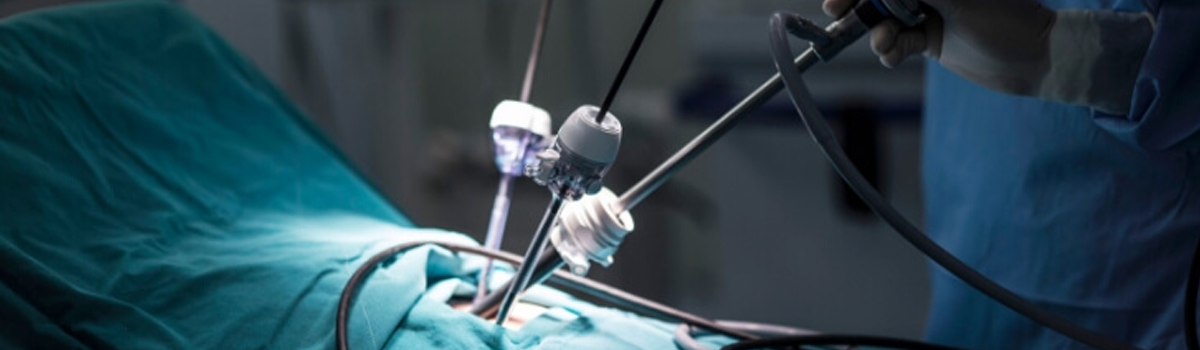
Minimal invasive surgery, also known as minimally invasive surgery or laparoscopic surgery, is a surgical technique that uses specialized instruments and small incisions to perform surgical procedures with less pain, scarring, and recovery time compared to traditional open surgery. This technique has revolutionized surgical care and has become increasingly popular in recent years.
The main advantage of minimal invasive surgery is that it causes less trauma to the body, resulting in less pain and a faster recovery time. Instead of making large incisions, surgeons make small incisions and insert specialized instruments and a tiny camera into the body to perform the surgery. This allows for more precise and targeted surgery, with less damage to surrounding tissues and organs.
Minimal invasive surgery can be used to treat a wide range of conditions, including gastrointestinal disorders, gynecologic disorders, urologic disorders, and many others. Common procedures include gallbladder removal, hernia repair, and hysterectomy.
The process of minimal invasive surgery begins with a thorough evaluation and diagnosis of the patient's condition. The surgeon will use imaging tests and other diagnostic tools to determine the best course of treatment. If minimal invasive surgery is deemed appropriate, the surgeon will create small incisions and insert specialized instruments and a tiny camera into the body to perform the surgery.
After the surgery, the patient will typically experience less pain and a shorter recovery time compared to traditional open surgery. The small incisions usually heal quickly, and patients can often return to their normal activities sooner.
Overall, minimal invasive surgery is a safe and effective alternative to traditional open surgery for many conditions. It offers patients less pain, less scarring, and a faster recovery time, allowing them to return to their normal activities sooner. If you are considering surgery, talk to your healthcare provider to see if minimal invasive surgery is right for you.