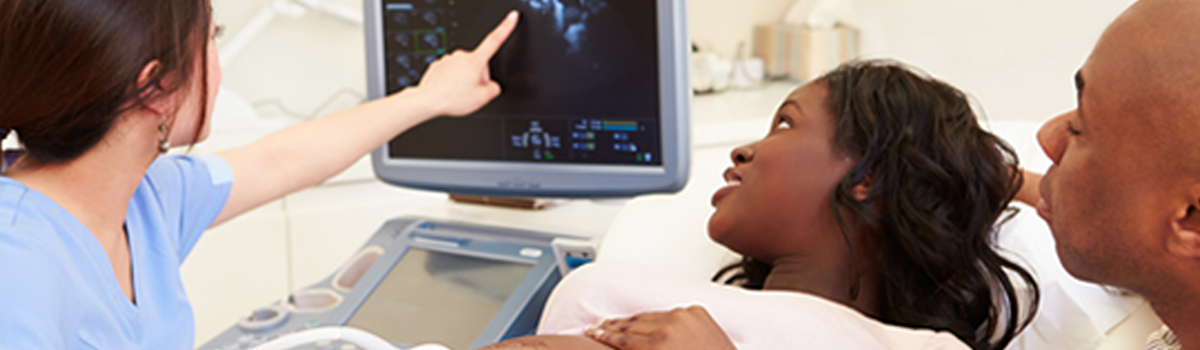
Sonography, also known as ultrasound imaging, is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the inside of the body. Sonographers, also known as ultrasound technicians, use a handheld device called a transducer to send sound waves into the body and then receive the echoes to produce images.
Sonography is commonly used for prenatal care, to monitor fetal development and detect any potential problems. It is also used to diagnose and monitor a variety of medical conditions, such as gallstones, liver disease, and cancers.
Some common types of sonography include:
Overall, sonography is a safe and non-invasive medical imaging technique that provides valuable diagnostic information for a variety of medical conditions. Sonographers play a critical role in performing sonography exams and providing accurate images for healthcare professionals to diagnose and treat their patients.